In this article, we will learn about what is MIG welding process or GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding). We will also learn its equipment, working principles, working, advantages, and disadvantages with the application. It is the most versatile process, mostly used in all types of manufacturing industries.
What is MIG Welding?
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process in which a consumable metal electrode is used to produce the electric arc to join the metal pieces together in the environment of a shielding gas. Shielding gas protects the weld from atmospheric contamination. Constant voltage, direct current power source is used to produce the arc.

- This welding was first invented in the year 1940 for welding aluminum and other non-ferrous materials.
- This process can be semi-automatic or automatic.
- It uses argon and helium as the shielding gas because these two are most economical and inert.
- The metal transfer in MIG welding takes place in four primary ways, and these are globular, short-circuiting, spray, and pulsed-spray. Each method has its own characteristic properties, advantages, and corresponding limitations.
Circuit Diagram of GMAW or MIG Welding Process

Main Equipment

The various equipment that is used in GMAW or MIG welding process are:
- A Welding Gun: It contains a wire electrode and a shielding gas supply.
- A Wire Feed Unit: It provides continuous wire feed metal electrode during welding operation.
- A Welding Power Supply: It is constant voltage power source whose one terminal is connected with the welding gun and the other is connected to the workpiece through clamping device.
- A Welding Electrode Wire: It is the metal wire which is used as the metal electrode in the GMAW welding.
- A Shielding Gas Supply: It is a cylinder which contains the shielding gas argon or helium.
Also Read:
- What is Arc Welding? How Arc Welding Works?
- What is TIG Welding Process or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
- Explosive Welding – Equipment, Types, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages with Application
Working Principle
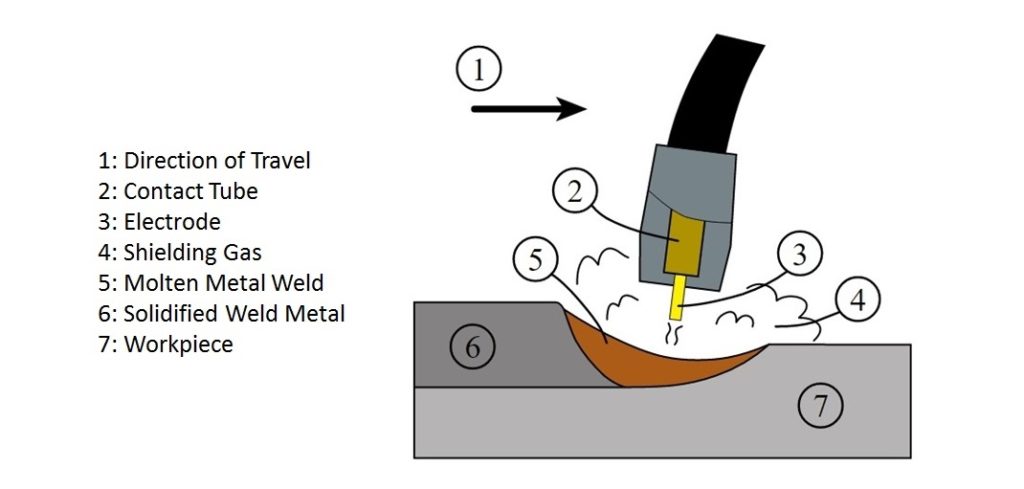
The MIG welding process is based on the principle that a consumable metal electrode is used to produce an arc in between the metal electrode and the workpiece. The arc so produced creates a large amount of heat and this heat is used to join the two metal pieces together. The whole process takes place under a shielding gas (argon or helium) to prevent the weld from atmospheric contamination.
Tool Style
In gas metal arc welding, the most commonly used electrode holders are
- Semi-Automatic Air-Cooled Holder: This type of holder uses compressed air to maintain the temperature at the required level. It uses low-level currents to make lap and butt joints.
- Semi-Automatic Water-Cooled: Its working is same us above holder but the difference is that it uses water for the cooling instead of compressed air. This uses higher level of currents to weld T or corner joints.
- Water Cooled Automatic Electrode Holder: It is a typical electrode holder and is used with automated equipment.
Power Supply
The MIG welding process or GMAW most commonly uses constant voltage, direct current power source for the welding. It can also use constant current systems and alternating current.
Shielding Gas:
The shielding gases are of two types- inert or semi inert. The shielding gases that are used in MIG welding are
- Argon and helium are inert and most cost effective shielding gas used in the MIG welding. Pure argon and helium is used to weld non-ferrous materials.
- The semi- inert gases are the mixtures of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen in the argon.
Working of MIG Welding
- In MIG welding process, the electrode wire from the wire feed unit and shielding gas supply is attached with the welding gun. The positive terminal of the DC power source is connected to the welding gun and the negative terminal is connected to a clamp.
- The clamp is connected to the workpiece to be joined. The welding gun is brought near the workpiece and as the trigger is pressed, the arc is produced at the tip of the welding gun. The arc produced melts the electrode wire and it gets deposited in between the two metal pieces to be joined and form a slag free weld.
- A shielding gas also starts to spread as the arc is produced. It protects the weld from reacting with atmospheric air and prevents weld from contamination.
- The weld formed in Gas Metal Arc Welding is free from slag. It is a clean and efficient process.
- This is the working of the GMAW or MIG welding process.
Advantages
- It is faster welding process.
- It has greater deposition rates.
- It provides better weld pool visibility.
- After the welding process is over, it requires less cleaning.
- A semi-skilled operator can operate MIG welding easily.
- It can be learned easily without much hard work.
- Absence of filler metal. The consumable metal electrode itself works as filler metal.
- The MIG welding process can be automated easily.
- It is a clean and efficient welding process.( no slag to chip off the weld)
Disadvantages
- Its initial setup cost is high.
- High maintenance costs because of more electronic equipment.
- It creates a radiation effect which is more severe.
- It is not suitable for outdoor welding.
- Thick metals cannot be welded by GMAW or MIG welding process.
- It is not capable to weld in all positions.
Application
The GMAW or MIG welding process are mostly used in automotive industries and pipe industries, building bridges and in the repair work.
We have studied about what is MIG Welding Process or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). Here we have discussed about working principle, equipment, working, advantages and disadvantages etc. If you have any query then comment us.